Did you know that farmers are more likely than the general population to die by suicide?
NY FarmNet is collaborating with county Cornell Cooperative Extension offices this fall to offer free, full day, in person Mental Health First Aid (MHFA) courses. Farmers, agribusiness workers, and anyone who interacts with the agricultural community in New York is encouraged to attend. Trainings run from 8am to 5pm, and lunch will be provided from a local eatery with a one hour break.
Mental Health First Aid teaches you how to identify, understand, and respond to signs of mental health and substance use challenges among adults. You’ll build skills and confidence you need to reach out and provide initial support to those who are struggling. You’ll also learn how to help connect them to appropriate support.
After the course, you will be able to:
• Recognize common signs and symptoms of mental health and substance use challenges.
• Understand how to interact with a person in crisis and connect them with help.
• Use self-care tools and techniques.
The instructors for these courses are part of a recently trained cohort that work within the NY agricultural community. They include representatives from NY FarmNet, Cornell Cooperative Extension, Farm Bureau, Young Farmers Coalition, NY Center for Ag Medicine and Health (NYCAMH), and Black Farmers United NYS.
Scheduled full day MHFA trainings for this fall include:
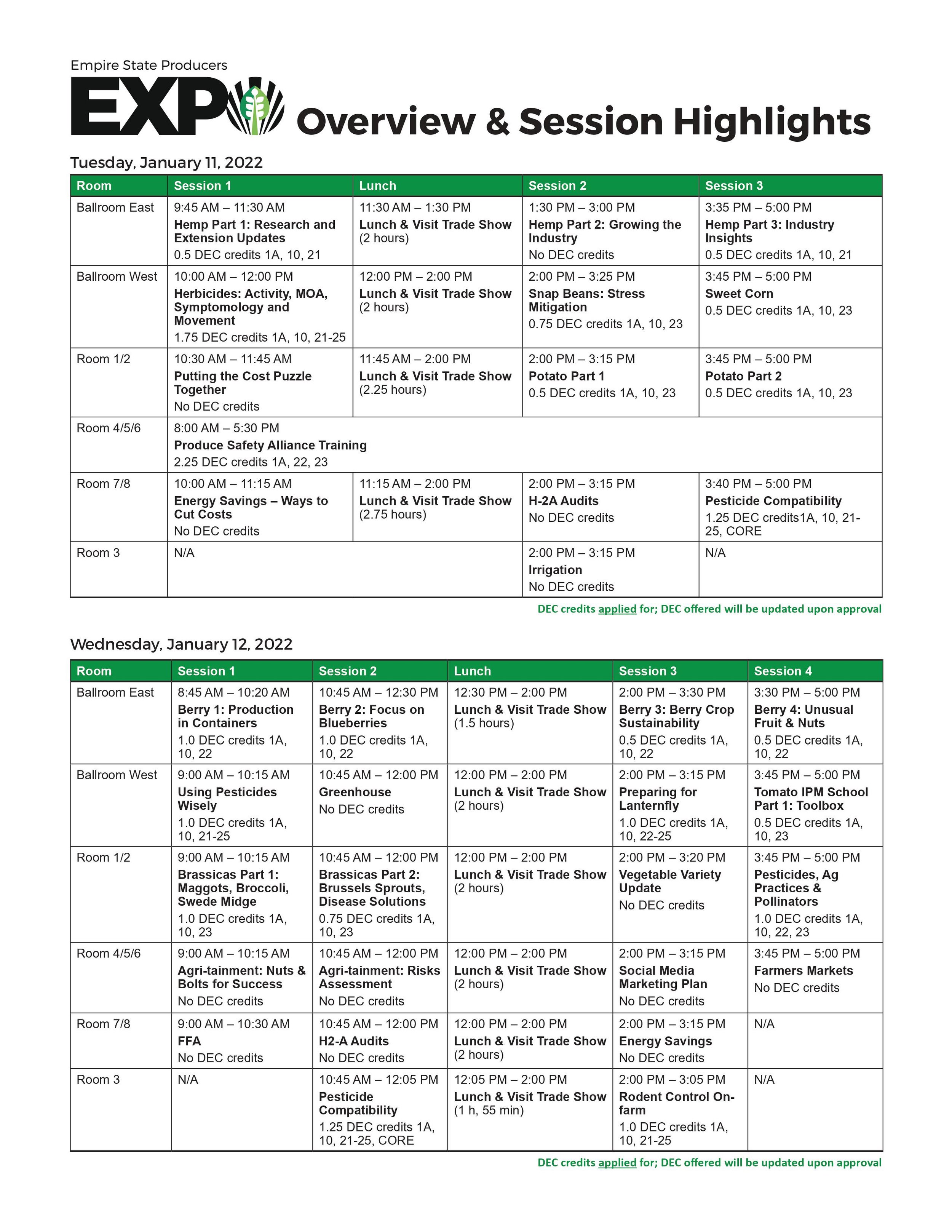
Tuesday, October 18 in Hudson/Columbia County
Wednesday, October 19 in Cortland/Cortland County
Friday, October 21 in Ithaca/Cornell University/Tompkins County
Tuesday, October 25 in Middletown/Orange County
Wednesday, November 2 in Binghamton/Broome County
Monday, November 7 in Lockport/Niagara County
Tuesday, November 8 in Fonda/Montgomery County
To register, go to www.nyfarmnet.org/trainings. If we don’t yet have a training scheduled in your area, check back soon, or contact NY FarmNet at 1-800-547-3276 or nyfarmnet@cornell.edu.
These free trainings are made possible by funding from the United States Department of Agriculture’s National Institute of Food & Agriculture. They have invested nearly $25 million in addressing farmer behavioral health on a state by state basis as part of the Farm and Stress Assistance Network (FRSAN) through state Departments of Agriculture.
This work is supported by 7 U.S.C. 5936, Section 7522 of FCEA of 2008, Farm and Ranch Stress Assistance Network (FRSAN), Grant No. 2021-70035-35550, from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, National Institute of Food and Agriculture.